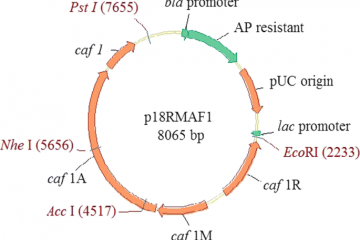
CUSABIO has been specialized in developing&producing antibodies for more than ten years, so we are confident that we have the expertise, experience as well as enabling technologies on antigen design and antibody purification to customize the high-quality antibodies that you are desiring.
Protein is an important component of all organisms. Each protein molecule consists of one or more polypeptide chains made of amino acids. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Different series of amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form protein chains. Each protein has a unique sequence of amino acids.
All the functions of proteins are dependent on their structures. Although information necessary for life is encoded by DNA or RNA, proteins perform a wide range of biological functions within organisms, including enzyme catalysis, defense, transport, support, motion, and regulation.
According to their functions in the body, proteins can be divided into different categories, such as antibodies, enzymes, cytokines, hormones, signaling peptides that transmit information into cells (messenger), structural component, and transport/storage proteins. Given the important functions of proteins, proteins have been studied intensively and applied widely.
In the past, the major way to obtain a specific protein was to isolate it from a natural source, which is generally inefficient and time-consuming. Recent advances in recombinant molecule biological techniques have made it possible to clone the DNA encoding a specific protein into an expression vector and express the protein in expression systems, such as bacteria, yeast, insect cells, and mammalian cells.
Simply put, recombinant proteins are translated products of exogenous DNA in living cells. The production of recombinant proteins generally contains two major steps: molecule cloning and protein expression. Currently, recombinant protein production is one of the most powerful techniques used in life sciences. Recombinant proteins have wide applications in medicine, research, and biotechnology, etc.
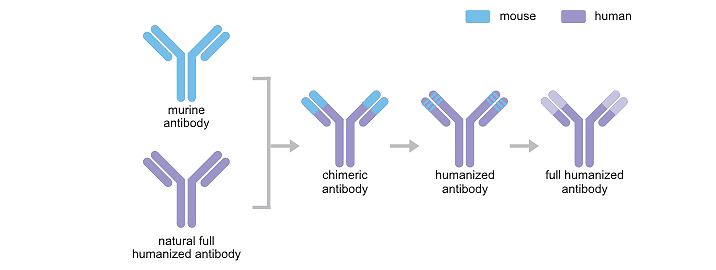
Development of Recombinant Antibody Cusabio
1. Medicine
2. Research
3. Biotechnology
4. The Latest Researches of Recombinant Proteins
- Recombinant proteins and diseases
- Recombinant proteins and vaccines
1. Medicine
Most human diseases are systemically or partially related to dysfuction of specific proteins. Therapeutic proteins provide important therapies for a variety of diseases, such as diabetes, cancer, infectious diseases, hemophilia, and anemia. Common therapeutic proteins include antibodies, FC fusion proteins, hormones, interleukins, enzymes, and anticoagulants.
There is a growing demand for recombinant proteins for therapeutic applications. Human proteins obtained through genetic engineering play a key role in therapeutic medicines market.
Currently, most of all recombinant therapeutic proteins are produced in mammalian cells because mammalian cells are capable of producing high-quality proteins similar to the naturally occurring ones. In addition, many approved recombinant therapeutic proteins are generated in E.coli due to its well-characterized genetics, rapid growth, and high-yield production.
Basically, therapeutic proteins can be classified into four groups.
Group I: Therapeutic proteins with enzymatic or regulatory activity. These proteins replace a protein that is deficient or abnormal, up-regulate an existing pathway, or provide a new function or activity.
Group II: Therapeutic proteins with special targeting activity. These proteins interfere with a molecule or organism or deliver other molecules.
Group III: Therapeutic proteins as vaccines. These proteins help protect against foreign agents, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
Group IV: Therapeutic proteins as diagnostics. These proteins are generally purified and recombinant proteins.
2. Research
Recombinant proteins help to elucidate the basic and fundamental principles of an organism. These molecules can be used to identify and locate the position of the protein encoded by a specific gene, and to uncover the function of other genes in various cellular activities such as cell signaling, metabolism, growth, replication and death, transcription, translation, and protein modification. Thus, recombinant proteins are frequently used in molecular biology, cell biology, biochemistry, structural and biophysical studies, and many other research fields.
Recombinant proteins are useful tools in understanding protein-protein interactions. They have proven performance in several laboratory techniques, such as ELISA, Western Blot, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Recombinant proteins can be used to develop enzymatic assays. When used in conjunction with a matched antibody pair, recombinant proteins can be used as standards such as ELISA standards. Moreover, recombinant proteins can be used as positive controls in Western blots.
3. Biotechnology
Recombinant proteins are also used in industry, food production, agriculture, and bioengineering. For example, in breeding industry, enzymes can be added to animal feed to increase the nutritional value of feed ingredients, reduce feed and waste management costs, support animal gut health, enhance animal performance and improve the environment. Besides, lactic acid bacteria (LAB) have been used for a long time for the production of fermented foods, and recently, LAB has been engineered for the expression of recombinant proteins, which would have wide applications such as improving human/animal digestion and nutrition.
However, recombinant proteins also have limitations.
* In some cases, the production of recombinant proteins is complex, expensive, and time-consuming.
* The recombinant proteins produced in cells may not be the same as the natural forms. This difference may reduce the effectiveness of therapeutic recombinant proteins and even cause side effects. Additionally, this difference may affect the results of experiments.
* A major concern for all recombinant drugs is immunogenicity. All biotechnologically produced therapeutics may exhibit some form of immunogenicity. It is difficult to predict the safety of novel therapeutic proteins.
Antigen-binding fragment (Fab fragment)
Upon treatment with papain, the rabbit IgG is cleaved at the core hinge, leading to the production of two identical Fab and an intact Fc. The Fab fragment retains the antigen-binding region and has a molecular weight of one-third of the full length of the antibody. At the same time, it has low immunogenicity due to its lack of Fc segment and is often used as a guide drug carrier and development.
* Single-chain variable fragment (scfv)
The scfv is a single-chain fragment of antibody V region formed by connecting the V region of heavy chain and light chain of antibody through a polypeptide linker. Since the scfv retains the Vregions of the full-length antibody, its antigen-binding site does not change and still has good binding specificity. In addition, the polypeptide linker of a scfv can be designed into other sites for metal chelation and linked drug as needed and is therefore a powerful tool in clinical applications.
* Multivalent antibody
Multivalent antibodies are antibodies that bind multiple antigens. At present, more attention is paid to “bispecific antibodies”, which is an artificial antibody contains two specific antigen conjugate site that can build a bridge between target cells and functional molecules, thus producing directional effect role.
The Latest Researches of Recombinant Proteins
Here, we numerate several researches of recombinant proteins from various fields.
4.1 Recombinant proteins and diseases
● Alpha-1-antitrypsin, a protein made by the liver, is secreted to the bloodstream, and then circulates the body to protect the lung. The patients who can not produce the protein usually regularly and quantitatively receieve an infusion of Alpha-1-antitrypsin protein, which is extracted from donor blood. Researchers from The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability at Technical University of Denmark have successfully produced Alpha-1-antitrypsin in CHO cells at scale. Furthermore, the researchers also improved the proteins by genetic techniques, thereby obtaining recombinant therapeutic proteins similar to human versions with a specific sugar-structure. It is likely to eliminate the need for human donors in the future.
● The Georgetown University-led study, published in Scientific Reports, reported that forced expression of the protein FGFBP3 (BP3 for short) in a laboratory strain of obese mice showed a remarkable reduction of their fat mass despite a genetic predisposition to eat all the time. The results of this study suggest that the protein FGFBP3 might offer novel therapy to reverse disorders associated with metabolic syndrome, such as type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease. But, because BP3 is a natural protein and not an artificial drug, clinical trials of recombinant human BP3 could begin after a final round of preclinical studies.
● PD-L2, one of the key players in immune checkpoint therapy, is the focus of the 2018 Nobel Prize for Physiology & Medicine. This work pioneered by Professor James P Allison from the USA and Professor Tasuku Honjo from Japan, has led to treatments for cancers, such as melanoma, lung cancer and others based upon immune checkpoint therapy. Recently, AMSBIO has added an important new product to its immunotherapy range – a PD-L2 / TCR activator – CHO Recombinant Cell Line.
4.2 Recombinant proteins and vaccines
● Human papillomavirus, referred to as HPV, not only causes cervical cancer in women, certain strains but also have been linked to head and neck cancers in men. Curently, Gardasil-9 vaccine is used to prevent the virus. Gardasil 9 is nine of these individual vaccines mixed into one, which can protect against multiple variants of HPV. But it is relatively expensive so that few people can afford it.
Researchers at the School of Life Sciences and the Biodesign Center for Immunotherapy, Vaccines and Virotherapy made an HPV VLP (virus-like particle) by attaching the L2 protein to a pre-existing hepatitis B virus-like particle, and then they obtained a recombinant immune complex by fusing the L2 protein to an antibody. They scaled up the vaccine in plants, getting a more affordable, plant-based vaccine that stimulates a strong, broadly protective immune response against the HPV virus. This vaccine model also can be applied to other infectious agents. Next, the researchers would like to test the safety and efficacy of the vaccine on humans or nonhuman primates.
[Linking template=”default” type=”products” search=”Recombinant Proteins” header=”1″ limit=”28″ start=”3″ showCatalogNumber=”true” showSize=”true” showSupplier=”true” showPrice=”true” showDescription=”true” showAdditionalInformation=”true” showImage=”true” showSchemaMarkup=”true” imageWidth=”” imageHeight=””]